- docs
- FlowFuse User Manuals
- Using FlowFuse
- Getting Started
- Static asset service
- Bill of Materials
- FlowFuse Concepts
- Instance States
- Changing the Stack
- Custom Hostnames
- Custom Node Packages
- DevOps Pipelines
- Environment Variables
- FlowFuse Expert
- FlowFuse File Nodes
- FlowFuse MQTT Nodes
- FlowFuse Project Nodes
- FlowFuse Tables
- Groups
- High Availability mode
- HTTP Access Tokens
- Instance Settings
- Logging
- persistent-context
- Role-Based Access Control
- Shared Team Library
- Snapshots
- Team Broker
- Teams
- User Settings
- FlowFuse API
- Migrating a Node-RED project to FlowFuse
- Device Agent
- Device Agent
- FlowFuse Device Agent Introduction
- Quick Start
- Installation
- Register your Remote Instance
- Running the Agent
- Deploying your Flows
- Hardware Guides
- FlowFuse Cloud
- FlowFuse Cloud
- FlowFuse Self-Hosted
- Quick Start
- Installing FlowFuse
- Overview
- Configuring FlowFuse
- DNS Setup
- Docker install
- Add Project Stacks on Docker
- Docker Engine on Windows
- Docker from AWS Market Place
- Docker on Digital Ocean
- Email configuration
- First Run Setup
- FlowFuse File Storage
- Install FlowFuse on Kubernetes
- Upgrading FlowFuse
- Administering FlowFuse
- Administering FlowFuse
- Configuring Single Sign-On (SSO)
- Licensing
- Monitoring
- Telemetry
- User Management
- Support
- Community Support
- Premium Support
- Debugging Node-RED issues
- Contributing
- Contributing to FlowFuse
- Introduction
- Adding Template Settings
- API Design
- Creating debug stack containers
- Database migrations
- FlowFuse Architecture
- Local Install
- State Flows
- Device Editor
- Instance states
- Invite External Users
- Project Creation
- Reset Password Flow
- Team creation Flow
- User Login Flows
- User Sign up Flow
- Team Broker
- Working with Feature Flags
Deploying Flows to the Device Agent
Before you're able to deploy your flows to your Remote Instance, you will have needed to have completed these steps:
- Install the Device Agent on the Device - installs Node-RED and other requirements in order to communicate with FlowFuse.
- Register the Remote Instance with FlowFuse - this step will have provided you with a
device.ymlfile to move to your Remote Instance. - Run the Device Agent - starts the Device Agent on the Remote Instance.
Deploying a Node-RED Snapshot to the Remote Instance From a Hosted Instance
To deploy a Node-RED Snapshot to the Remote Instance:
- Create a snapshot - a point-in-time backup of the Node-RED flows and configuration.
- Mark that snapshot as the Remote Instance Target snapshot.
This model allows you to develop your flows in FlowFuse and only push it out to the registered Remote Instances when you're happy with what you've created.
Starting Node-RED on the Remote Instance without deploying a snapshot
A Remote Instance can be assigned to an application without a snapshot being deployed to it.
In this mode, the Remote Instance will start Node-RED with a default set of flows that can be edited on the Remote Instance see Editing the Node-RED flows on a Remote Instance that is assigned to an application below
Editing the Node-RED flows on a Remote Instance that is assigned to an instance
When running in the default of Fleet Mode, the device agent does not allow local access to the Node-RED editor. This ensures the Remote Instance is running the deployed snapshot without modification.
When running on FlowFuse Cloud, or a premium licensed FlowFuse instance (with the MQTT broker enabled the Remote Instance can be placed in Developer Mode that enables remote access to the editor.
This can then be used to develop the flows directly on the Remote Instance and a new snapshot generated from the Remote Instance that can be deployed to other Remote Instances in the application.
Whilst in Developer Mode the Remote Instance will not receive new updates from the platform when new snapshots are deployed.
Accessing the Editor
- Once developer mode is enabled, click the Enable button next to the 'Editor Access' option
- When the editor is available, the Editor button in the header will become active and will take you to the device editor.
Creating a Remote Instance Snapshot
To create an instance snapshot from the Remote Instance use the Create Snapshot button in the Developer Mode options panel.
You will be prompted to give the snapshot a name and description. See Snapshots for more information about working with snapshots.
Editing the Node-RED flows on a Remote Instance that is assigned to an application
Access to the editor is only available when:
-
The Remote Instance is in Developer Mode
-
When running on FlowFuse Cloud, or a premium licensed FlowFuse instance (with the MQTT broker enabled the Remote Instance can be placed in Developer Mode that enables remote access to the editor.
-
Local access to the editor can be enabled by defining a Username & Password in the Device Settings -> Security and enabling "Allow offline access"
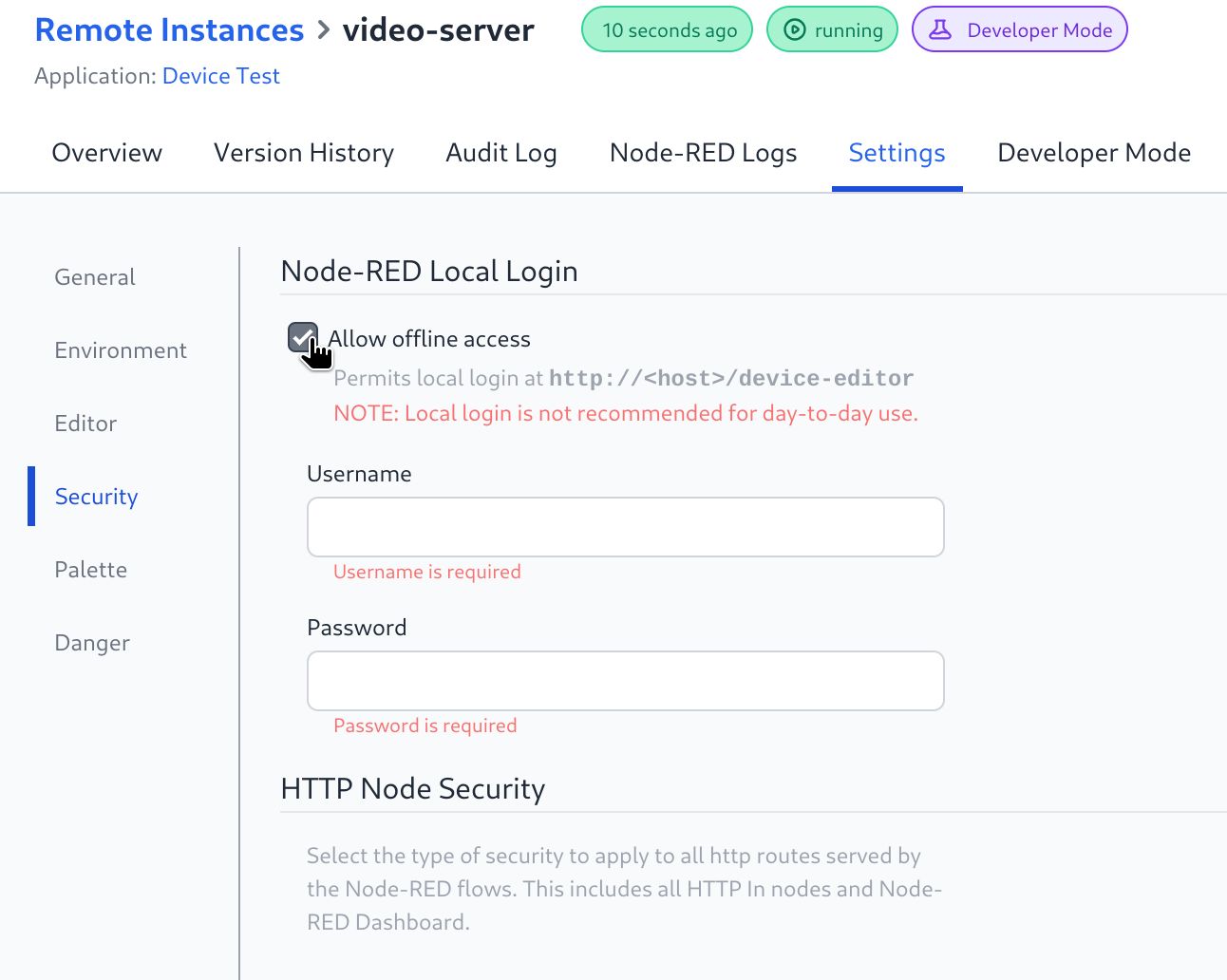
Whilst in Developer Mode the Remote Instance will not receive new updates from the platform.
Enabling Developer Mode
- Go to your team's Remote Instances page.
- Select the Remote Instance you want to edit by clicking its name.
- Click the "Developer Mode" button to enable developer mode.
- Once enabled, Developer Mode options are available under the tab labelled "Developer Mode" on the Remote Instance page.
Accessing the Editor
- Once developer mode is enabled, click the Enable button next to the 'Editor Access' option
- When the editor is available, the Editor button in the header will become active and will take you to the Remote Instance editor.
Creating a Remote Instance Snapshot
To create a snapshot from an application owned Remote Instance use the Create Snapshot button in the Developer Mode options panel.
You will be prompted to give the snapshot a name and description. See Snapshots for more information about working with snapshots.
Auto Remote Instance Snapshots
For Remote Instances that are assigned to an application, the platform will automatically create a snapshot of the Remote Instance when it detects flows modified. This snapshot will be created with the name "Auto Snapshot - yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm-ss". Only the last 10 auto snapshots are kept, others are deleted on a first in first out basis.
Custom Node Catalogues
For Remote Instances that want to make use of custom node catalogues, these can be configured under the Remote Instance settings page on the Palette tab
.npmrc file
Likewise for Remote Instances that need to be provided with a custom .npmrc file to allow access to a custom npm registry or to provide an access token this can also be set on the Remote Instance settings Palette tab
Important Notes
- Remote access to the editor requires Device Agent v0.8.0 or later.
- The Web UI requires Device Agent v0.9.0 or later.
- Assigning a Remote Instance to an application requires Device Agent v1.11.0 and FlowFuse v1.11.0 or later.
- Snapshots of Remote Instances assigned to an application are supported in FlowFuse V1.12.0 or later.
- Deploying a snapshot from a different Hosted Instance or Remote Instance to an application owned Remote Instance is supported in FlowFuse V1.13.0 or later.
- When a Remote Instance is assigned to a Hosted Instance:
- It must first have a snapshot applied before editor access is possible.
- Disabling Developer Mode and returning to Fleet Mode will cause the Remote Instance to check in with the platform. If the Remote Instance flows have changed, it will be reloaded with the current target snapshot assigned to that Remote Instance, causing any changes made in Developer Mode to be overwritten. Therefore, it is recommended to create a snapshot of the changes before disabling Developer Mode.
- When a Remote Instance is assigned to an application:
- It will start with a set of default flows.
- The Remote Instance will not receive any updates from the platform while in Developer Mode.
- The Remote Instance must be online and connected to the platform to enable "Editor Access".
- To minimise server and Remote Instance resources, it is recommended to disable "Editor Access" when not actively developing flows on a Remote Instance.
- Auto snapshots were introduced in FlowFuse V2.1.
- Auto snapshots are only supported for Remote Instance assigned to an application.
- If an auto snapshot is set as the target snapshot for a Remote Instance or assigned to a pipeline stage, it will not be auto cleaned up meaning it is possible to have more than 10 auto snapshots.
Table of Contents
- Deploying a Node-RED Snapshot to the Remote Instance From a Hosted Instance
- Starting Node-RED on the Remote Instance without deploying a snapshot
- Editing the Node-RED flows on a Remote Instance that is assigned to an instance
- Editing the Node-RED flows on a Remote Instance that is assigned to an application