Why UNS needs Pub/Sub
Discover How Pub/Sub Transforms Unified Namespace into a Scalable, Real-Time Data Powerhouse for Modern Manufacturing.
As the manufacturing industry evolves and becomes increasingly connected through the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), the concept of a Unified Namespace (UNS) has emerged as a critical architecture for centralizing and organizing data. UNS serves as a central reference point where all operational data, from machines to the enterprise, can be accessed in a consistent and structured way. Over time, more and more manufacturers have adopted UNS to simplify data integration and improve real-time visibility across systems.
If you're unfamiliar with UNS, please read our Introduction to Unified Namespace for a basic understanding of UNS.
If you're familiar with or already using a UNS, you might be asking: Why does a UNS need Pub/Sub? Here, we’ll explore how combining the Pub/Sub model with a Unified Namespace can help manufacturers streamline data flow, reduce latency, and enable more responsive and scalable operations.
# What is Pub/Sub?
Before discussing why Publish/Subscribe (Pub/Sub) is essential for a UNS, let's first define the Pub/Sub model.
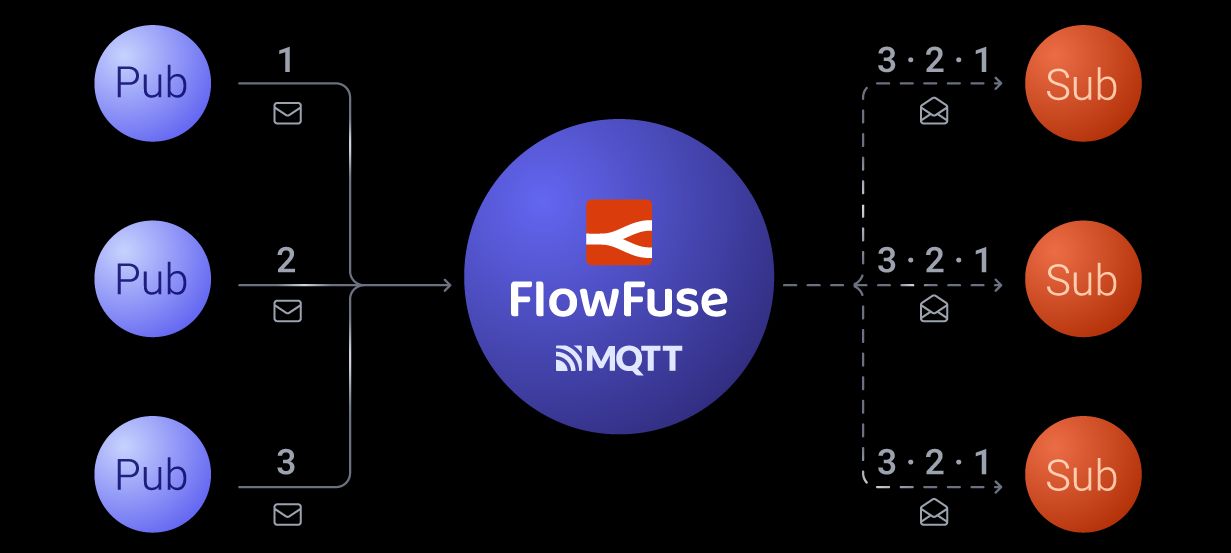
The Pub/Sub model is a way for systems to communicate where one component, called the publisher, sends messages to a central system ( Broker such as MQTT, RabitMQ, and Kafka ), and other components, called subscribers, receive those messages. The publisher doesn’t need to know who the subscribers are, and the subscribers don’t know who the publishers are. The central system, or broker, ensures the right messages go to the right subscribers based on their interests.
Additionally, it’s important to note that the roles of publisher and subscriber are not mutually exclusive. A component can act as a publisher in one context, sending messages to the broker, and as a subscriber in another, receiving messages from the broker.
# Why Does a UNS Need Pub/Sub?
Now that you have a basic understanding of Pub/Sub, let’s dive into why this architecture is essential for a Unified Namespace.
# Decoupling Producers and Consumers with Flexible Communication
In traditional manufacturing setups, various systems and machines often operate in silos, requiring point-to-point connections for communication. This means each device or system must be directly linked to others, which quickly becomes complex and cumbersome as the number of systems grows. Point-to-point integrations are hard to scale because each new device needs a dedicated connection. This not only makes data harder to access but also blocks innovation by creating dependencies between systems.
To learn more about how point-to-point systems restrict innovation, please read the article: Why the Automation Pyramid Blocks Digital Transformation
The Pub/Sub model provides a more scalable solution. In this model, publishers (such as IoT devices or machines) generate data and send it to a central system. Subscribers (other systems, applications, or users) then receive only the data relevant to them. Crucially, the publishers and subscribers do not need to know about each other, relying instead on a central Namespace to distribute the data efficiently.
By using Pub/Sub in a UNS, industries can create a single reference point for all data, enabling systems to subscribe to the data streams they need, without direct connections to every other system. For example, a production line monitoring system can easily access data from temperature sensors, pressure gauges, and robotic arms without the need for complex point-to-point integrations.
Unlike point-to-point systems, the Pub/Sub model allows for flexible communication—whether one-to-one, one-to-many, or many-to-many—without the need for direct connections between each system. This flexibility ensures that as your factory evolves, new devices and applications can easily be integrated into the UNS, driving innovation.
# Event-driven and Asynchronous Communication
The Pub/Sub model is particularly well-suited for event-driven architectures, where systems react to changes in data rather than periodically polling for updates. This is important in environments where responsiveness is key—such as in predictive maintenance, supply chain optimization, or automated decision-making.
For instance, a predictive maintenance system can subscribe to real-time sensor data from machines in a UNS. When the system detects an anomaly (e.g., a machine vibration out of normal parameters), it can immediately trigger an alert or maintenance action. This type of asynchronous communication is more efficient and scalable than synchronous polling or direct communication between producers and consumers.
# Less Delay, More Efficiency
In industries where IIoT-enabled operations are prevalent, real-time data is essential for effective decision-making. Traditional systems often introduce delays due to multiple layers of data collection, storage, and processing. These delays can result in inefficiencies such as slow machine adjustments, missed production targets, or equipment failures.
The Pub/Sub model reduces latency by immediately pushing data to subscribers as soon as it’s available. There’s no need for systems to poll or wait for periodic updates. Instead, they can respond to real-time events as soon as they occur.
For instance, in a smart factory, if a machine’s temperature exceeds a threshold, a maintenance system could instantly react by scheduling a technician, triggering an alert, or even pausing operations. Without Pub/Sub, the system would have to rely on polling mechanisms, which are less efficient and often introduce unnecessary delays.
In real-time environments, these immediate actions can make the difference between preventing costly downtime or catching a problem too late.
# Easy to Scale as You Grow
Manufacturers are always expanding—whether by adding more machines to the production line, introducing new automation systems, or scaling up to handle more products or more data. Scaling traditional systems to keep up with this growth can be complex and costly, especially when new devices or technologies need to be integrated.
The beauty of Pub/Sub is that it scales effortlessly. When new machines or sensors are introduced, they simply publish their data to the namespace. No complex reconfiguration or integration is required. Similarly, if a new application needs to access this data, it can simply subscribe to the relevant streams.
For example, consider a car manufacturer adding new robotic arms to the production line. These robots can publish real-time performance data, such as arm movement speeds, energy consumption, and fault alerts, directly into the UNS. The factory’s existing data systems can then subscribe to this new data without requiring changes to the entire system, making integration quick and cost-effective.
This level of scalability helps manufacturers keep up with growth without worrying about complex system upgrades or slowdowns.
# Making Your Systems More Reliable
In manufacturing, system downtime is costly. However traditional, monolithic systems often rely on point-to-point connections, which can create vulnerabilities. If one part of the system goes down, it can bring down other systems or halt production entirely.
With a Pub/Sub architecture, this is less of a concern. If one publisher (like a sensor or machine) fails or goes offline, the rest of the systems can continue operating as normal. Other sensors or machines can continue to send their data, and subscribers can still receive real-time updates from other sources.
Consider a delivery system in a Point-to-Point setup, all vehicles send data directly to a central dispatch system. If the central dispatch system fails, data from all vehicles is lost. In a Pub/Sub setup, vehicles send their data to a central namespace instead of directly to the dispatch system. If the central dispatch system fails, it doesn’t result in data loss. Vehicles can still send their updates.
This decoupling of systems improves resilience, meaning that your factory can continue running smoothly even if individual components experience issues.
While the broker is a critical part of the Pub/Sub system and can also go down, this risk can be mitigated. Strategies such as high-availability brokers, failover mechanisms, and clustered deployments can be implemented to prevent downtime and ensure uninterrupted data flow.
# Taking Action
As we've discussed, the Pub/Sub model is a game-changer for Unified Namespace architectures in the manufacturing industry. One of the most widely adopted protocols for implementing Pub/Sub is MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport). MQTT is known for its simplicity, efficiency, and low-bandwidth requirements, making it an ideal choice for Industrial applications.
To help you leverage the power of MQTT in your manufacturing operations along with Node-RED, Flowfuse offers a robust MQTT broker service. Now, Flowfuse will not only help you build, scale, and manage Node-RED solutions, collaborate across teams, and manage edge devices, but it will also simplify your integration of IIoT data streams into your Unified Namespace. For more information on how our FlowFuse MQTT broker Service, read our MQTT Broker Service Announcement.
Get started with this article Building UNS with FlowFuse.
# Conclusion
Integrating Pub/Sub with a Unified Namespace enhances manufacturing operations by enabling real-time data flow, reducing latency, and improving scalability. This combination ensures efficient, resilient, and future-ready systems, empowering manufacturers to stay competitive in the IIoT era.
Curious about how FlowFuse can simplify building your Unified Namespace?
Sign Up for FlowFuse Now to Get StartedWritten By:
Published on:
Related Articles:
- Designing a Clear Topic Structure for Your UNS
- Building a Unified Namespace (UNS) with FlowFuse
- The Death of Point-to-Point: Why You Need a Unified Namespace
- Managing MQTT Connections at Scale in FlowFuse
- Why FlowFuse is the Complete Toolkit For Building UNS?